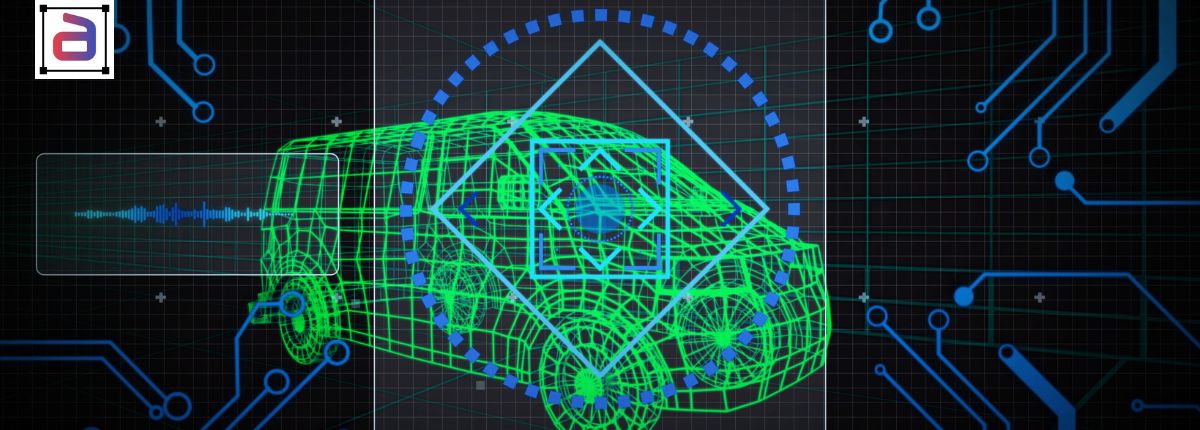
3D annotation for robotic navigation is critical to enabling computer vision systems to operate reliably in dynamic industrial and robotic environments. As manufacturers and robotics teams deploy autonomous systems for navigation, picking, and material handling, AI models must understand depth, spatial relationships, and object positioning with high precision. Structured 3D annotation provides the visual ground truth required to train robots to navigate complex spaces safely and efficiently.
For robotics engineers and automation leaders, 3D cuboid annotation is not theoretical. It is a foundational requirement for deploying navigation-capable robotic systems in real-world environments.
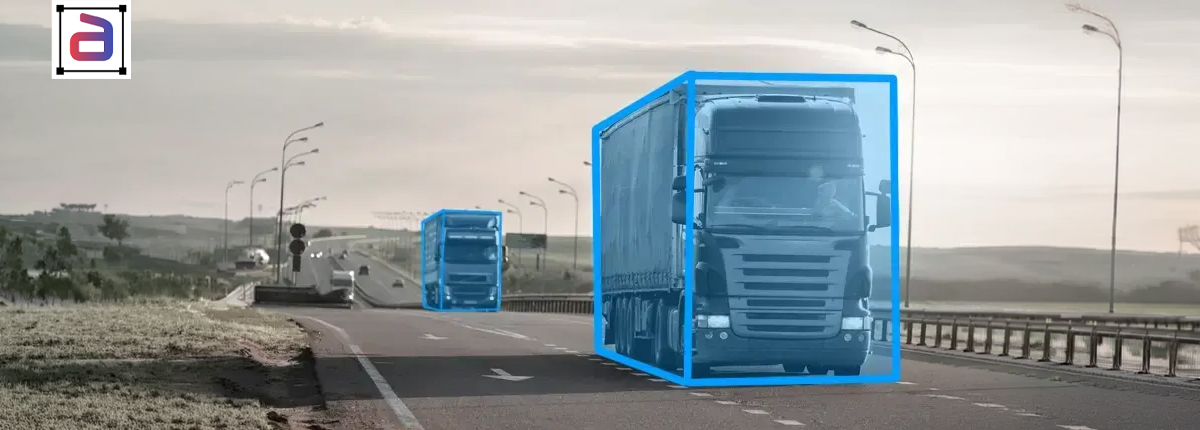
Why Manufacturing AI Depends on Bounding Boxes
Manufacturing environments are visually dense and operationally unforgiving. Machines move continuously, components overlap, and lighting conditions vary across shifts and facilities. 3D annotation for robotic navigation helps models learn how to localize relevant objects despite these challenges.
By defining clear object boundaries, image boxes enable AI systems to distinguish between acceptable variation and true anomalies, which is essential for the reliability of automated systems.
Core Manufacturing Use Cases for Image Boxes
Part Detection and Identification
Bounding box annotation enables AI systems to identify individual components on assembly lines, even when parts are partially occluded or appear in different orientations.
Defect Detection and Quality Inspection
Image boxes help models focus on areas where defects are likely to occur, supporting automated inspection processes that reduce manual checks and improve consistency.
Safety Monitoring and Compliance
Manufacturing AI uses bounding boxes to detect human presence near hazardous machinery, identify missing safety equipment, and enforce compliance protocols.
Robotic Guidance and Automation
Robots rely on accurately labeled images to locate parts, align tools, and execute tasks with minimal error, making bounding boxes a key input for robotic vision systems.
Image Challenges Unique to Factory Environments
Factory images introduce challenges not typically found in consumer datasets. These include motion blur from high-speed machinery, glare from metal surfaces, dust or debris, and highly repetitive visual patterns.
3D annotation for robotic navigation must be applied with discipline to ensure models learn relevant signals rather than environmental noise.
Precision Requirements in Industrial Annotation
Manufacturing tolerances are often measured in millimeters. Loose or inconsistent bounding boxes can cause automation systems to misinterpret object positions or miss defects entirely.
As a result, image box annotation for manufacturing requires tighter guidelines, stricter quality thresholds, and domain-aware review processes compared to general-purpose datasets.
Integrating Bounding Box Data into Automation Systems
Annotated image data feeds directly into vision models that integrate with programmable logic controllers, robotics platforms, and manufacturing execution systems.
Consistency in bounding box annotation ensures that AI outputs remain stable when deployed across multiple production lines or facilities.
Scaling Annotation Across Plants and Product Lines
As manufacturers expand automation initiatives, annotation requirements grow rapidly. New products, line modifications, and facility rollouts all require updated training data.
Managed bounding box services help industrial teams scale annotation efforts without disrupting production schedules or overloading internal resources.
How Annotera Supports Manufacturing AI Programs
Annotera delivers bounding boxes for manufacturing through trained annotation teams familiar with industrial use cases. Annotation workflows are governed by detailed guidelines and multi-layer quality assurance tailored to factory automation needs.
This approach allows manufacturers to maintain robotics annotation accuracy while scaling datasets across multiple plants, product types, and inspection scenarios.
Conclusion
Training AI for factory automation requires more than advanced algorithms. It requires high-quality visual data grounded in precise, consistent annotation practices.
3D annotation for robotic navigation provides the structured foundation that enables reliable detection, inspection, and automation across industrial environments.
Looking to deploy or scale AI-driven automation on the factory floor? Partner with Annotera for expert-led bounding-box annotation, designed for manufacturing precision and operational reliability.